Grey Space vs White Space: Understanding Data Centre Infrastructure Zones
Grey Space vs White Space: Understanding Data Centre Infrastructure Zones
The Critical Distinction That Defines Data Centre Architecture
The fundamental division between grey space and white space represents one of the most important yet poorly understood concepts in data centre design and operations. This architectural distinction influences everything from construction methodology and equipment selection to operational procedures and maintenance strategies, yet the implications of grey/white space planning decisions often remain invisible until operational challenges emerge.
Modern hyperscale facilities amplify the importance of optimal grey/white space design as higher power densities, advanced cooling technologies, and stringent efficiency requirements demand precise coordination between infrastructure zones. The interdependencies between grey space systems and white space performance create design challenges that require deep understanding of both mechanical engineering principles and operational requirements.
At AuditCo, our partnership with Qcloud has enhanced our capability to deliver comprehensive grey/white space design and installation services that optimise the relationship between infrastructure zones. This collaboration combines our expertise in quality assurance and compliance verification with Qcloud’s specialist knowledge of hyperscale infrastructure design, ensuring that grey/white space coordination supports optimal facility performance throughout the operational lifecycle.
Defining the Fundamental Infrastructure Zones
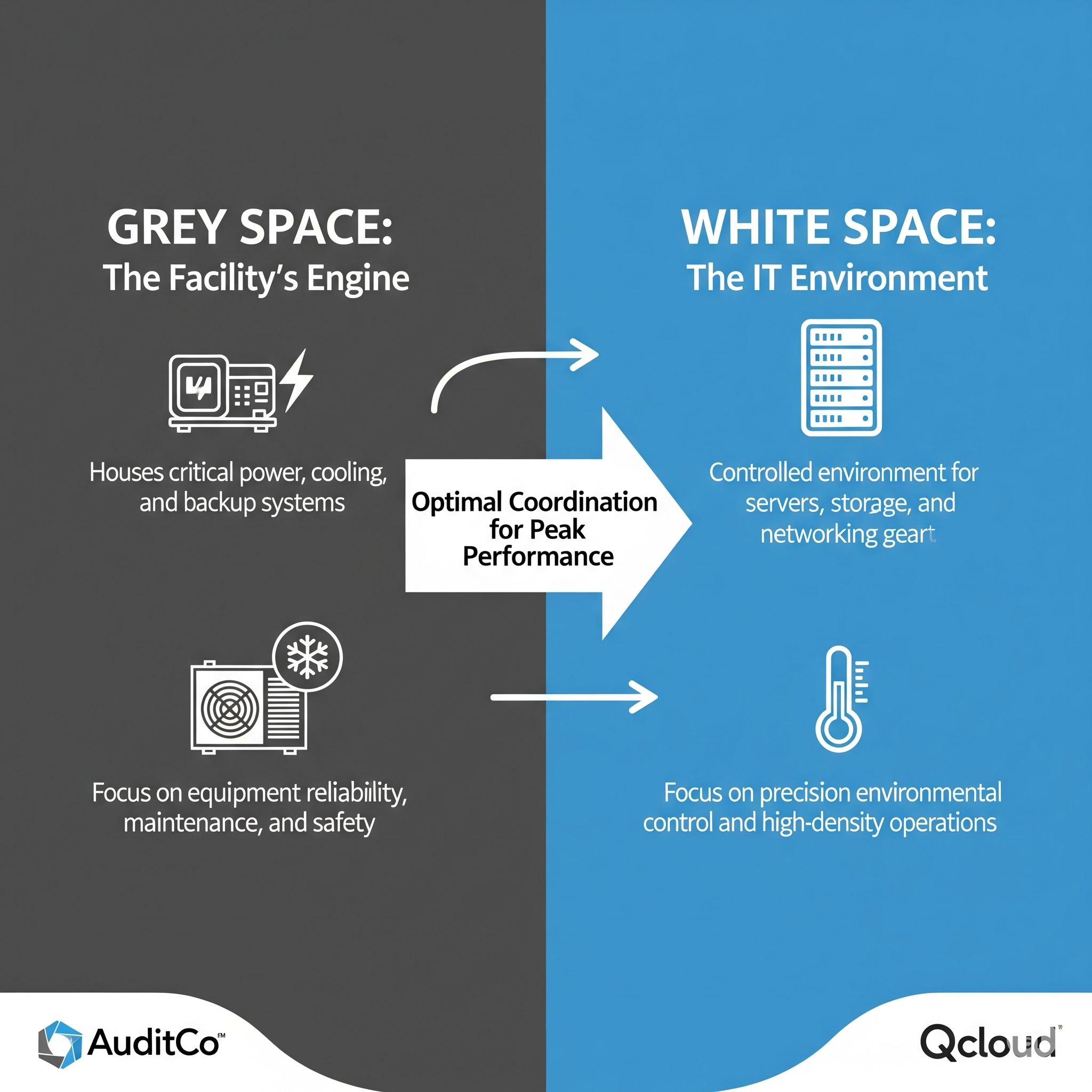
Grey space encompasses all the supporting infrastructure that enables white space operations but remains separate from the controlled environment where IT equipment operates. This includes electrical switchgear, transformers, uninterruptible power supplies, cooling plant equipment, backup generators, fuel systems, and building management infrastructure that collectively provide the power, cooling, and control systems required for data centre operations.
The design of grey space areas requires careful consideration of maintenance accessibility, equipment lifecycle management, and operational safety whilst maintaining the compact footprint demanded by modern facility economics. Grey space design must accommodate substantial mechanical and electrical equipment whilst providing the access corridors, lifting capabilities, and safety systems required for ongoing maintenance operations.
White space represents the controlled environment where servers, storage systems, and networking equipment operate under precisely maintained temperature, humidity, and airflow conditions. This environment requires exceptional attention to environmental control, power distribution precision, and cable management systems that support high-density IT operations whilst maintaining the flexibility required for ongoing equipment changes.
The relationship between grey and white space zones significantly influences facility efficiency, operational costs, and maintenance procedures. Optimal design requires careful coordination of power distribution pathways, cooling system integration, and monitoring system interfaces that enable efficient grey space operations whilst maintaining the environmental precision required for white space performance.
Understanding the distinct requirements of each zone enables design decisions that optimise overall facility performance rather than sub-optimising individual systems. The most successful hyperscale facilities demonstrate sophisticated grey/white space coordination that maximises infrastructure efficiency whilst maintaining operational flexibility and maintenance accessibility.
Grey Space Infrastructure and Design Principles
Electrical infrastructure within grey space areas includes the substantial switchgear, transformers, and power conditioning equipment that convert utility power into the clean, reliable electricity required for IT operations. The design of grey space electrical systems must balance equipment accessibility, safety requirements, and space efficiency whilst providing the redundancy and monitoring capabilities required for mission-critical operations.
Medium voltage switchgear represents the first stage of power conditioning within most hyperscale facilities, where utility power is distributed to multiple transformer systems that provide the voltage levels required for different facility systems. Grey space design must accommodate the substantial physical requirements of medium voltage equipment whilst providing the safety clearances, ventilation, and maintenance access required for reliable operations.
Transformer systems within grey space areas convert medium voltage power to the lower voltages required for IT equipment, cooling systems, and facility infrastructure. The heat generated by transformer operations requires sophisticated ventilation systems that maintain optimal operating temperatures whilst managing the acoustic emissions that can affect both facility operations and community relations.
Uninterruptible power supply systems bridge the gap between grey space power conditioning and white space power distribution, providing the power quality and continuity required for IT operations. UPS placement within grey space areas must consider heat rejection requirements, maintenance accessibility, and battery management systems whilst maintaining the compact footprint required for efficient facility design.
Backup generator systems represent perhaps the most challenging aspect of grey space design, requiring substantial equipment installations, fuel storage systems, exhaust management, and acoustic control measures. Generator placement must consider maintenance access, fuel delivery logistics, exhaust dispersion, and noise management whilst providing the reliability and capacity required for facility operations.
Cooling plant equipment within grey space areas includes chillers, cooling towers, pumping systems, and heat exchangers that remove the substantial thermal loads generated by IT equipment. The design of cooling plant installations requires careful consideration of equipment access, refrigerant management, water treatment systems, and control system integration whilst maintaining the efficiency levels demanded by modern sustainability requirements.
White Space Design and Environmental Control
Power distribution within white space areas represents the final stage of electrical infrastructure, where conditioned power is delivered to IT equipment through sophisticated distribution systems that provide monitoring, protection, and flexibility for changing operational requirements. White space power design must balance distribution efficiency, installation flexibility, and safety requirements whilst maintaining the compact footprint required for high-density operations.
Raised floor systems within white space areas serve multiple critical functions, providing structured pathways for power and data cabling whilst enabling efficient cooling air distribution throughout the facility. The design of raised floor systems requires careful consideration of load distribution, airflow management, cable organisation, and access requirements that support both current operations and future modifications.
Environmental control systems within white space areas maintain the precise temperature, humidity, and airflow conditions required for optimal IT equipment performance. The integration of environmental control systems with grey space cooling plant requires sophisticated control algorithms that maintain white space conditions efficiently whilst optimising facility-wide energy consumption.
Cable management within white space areas significantly influences both operational efficiency and future expansion capabilities. The organisation of power, data, and fibre optic cables requires systematic approaches that provide protection, accessibility, and flexibility whilst maintaining the clean, professional appearance that characterises world-class facilities.
Monitoring systems within white space areas provide real-time visibility into environmental conditions, power consumption, and equipment status that enables proactive facility management. The integration of white space monitoring with grey space systems provides comprehensive facility visibility whilst maintaining the security and reliability required for mission-critical operations.
Fire protection systems within white space areas require specialised detection and suppression technologies that protect sensitive IT equipment whilst ensuring personnel safety. The coordination of white space fire protection with facility-wide safety systems requires careful consideration of detection sensitivity, suppression agent selection, and emergency response procedures.
The Interface Between Infrastructure Zones
Power distribution interfaces between grey and white space represent critical design decisions that influence both system efficiency and operational flexibility. The location and design of electrical distribution equipment affects power quality, system reliability, and maintenance procedures whilst influencing the physical relationship between infrastructure zones.
Cooling system interfaces require careful coordination of heat rejection pathways, control system integration, and monitoring capabilities that enable efficient thermal management across infrastructure zones. The design of cooling interfaces affects both system efficiency and operational procedures, making coordination between grey and white space systems essential for optimal performance.
Control system integration enables coordinated facility management that optimises performance across infrastructure zones whilst maintaining the monitoring capabilities required for proactive maintenance and fault detection. The design of control system interfaces affects both operational efficiency and troubleshooting capabilities throughout the facility lifecycle.
Access control between infrastructure zones requires security measures that protect sensitive white space areas whilst enabling efficient maintenance operations in grey space areas. The design of access control systems must balance security requirements with operational efficiency, ensuring that maintenance activities can be conducted safely without compromising IT operations.
Emergency response procedures require coordination between infrastructure zones to ensure personnel safety whilst maintaining facility operations during emergency conditions. The design of emergency systems must consider evacuation procedures, system shutdown sequences, and recovery operations that span both grey and white space areas.
Materials and Equipment Selection Strategies
Grey space equipment selection requires careful consideration of reliability, maintainability, and lifecycle costs that influence long-term facility operations. The selection of mechanical and electrical equipment affects both capital costs and operational expenses, making comprehensive lifecycle analysis essential for optimal grey space design.
Cooling equipment selection within grey space areas must balance efficiency, reliability, and maintenance requirements whilst considering refrigerant regulations, noise control, and future expansion capabilities. The choice between different cooling technologies affects both facility performance and operational procedures throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Electrical equipment selection for grey space installations requires consideration of protection capabilities, monitoring features, and maintenance requirements that influence both safety and operational efficiency. The selection of switchgear, transformers, and protection systems affects facility reliability whilst influencing maintenance procedures and operational costs.
White space equipment selection focuses on precision, reliability, and flexibility requirements that support high-density IT operations whilst enabling efficient facility management. The selection of power distribution, environmental control, and monitoring equipment affects both operational efficiency and future expansion capabilities.
Installation methodology differs significantly between grey and white space areas, with grey space installations typically requiring heavy lifting equipment, substantial access requirements, and coordination with building systems. White space installations demand precision, cleanliness, and minimal disruption to ongoing operations, requiring different installation approaches and quality control procedures.
Quality control procedures must address the distinct requirements of each infrastructure zone whilst ensuring coordination between systems that span multiple areas. Grey space quality control focuses on mechanical integrity, electrical safety, and system performance, whilst white space quality control emphasises precision, cleanliness, and environmental control.
Operational Considerations and Maintenance Planning
Maintenance procedures differ substantially between infrastructure zones, with grey space maintenance typically involving larger equipment, longer outage windows, and coordination with utility systems. The planning of grey space maintenance requires consideration of redundancy requirements, access procedures, and safety systems that enable maintenance activities without compromising facility operations.
White space maintenance focuses on precision, minimal disruption, and rapid restoration of optimal environmental conditions. The planning of white space maintenance requires careful coordination with IT operations, environmental control systems, and monitoring capabilities that enable maintenance activities whilst maintaining service continuity.
Staff training requirements vary between infrastructure zones, with grey space operations requiring expertise in mechanical systems, electrical safety, and equipment maintenance procedures. White space operations demand understanding of environmental control, IT infrastructure, and precision maintenance techniques that maintain optimal conditions for sensitive electronic equipment.
Emergency response procedures must address the distinct characteristics of each infrastructure zone whilst ensuring coordinated facility response during emergency conditions. Grey space emergency procedures focus on equipment safety, personnel protection, and system isolation, whilst white space procedures emphasise environmental protection, equipment continuity, and rapid restoration of optimal conditions.
Performance monitoring systems must provide visibility into both infrastructure zones whilst enabling analysis of system interactions and optimisation opportunities. The design of monitoring systems affects both operational efficiency and troubleshooting capabilities, making comprehensive monitoring essential for optimal facility performance.
Documentation requirements differ between infrastructure zones, with grey space documentation focusing on equipment specifications, maintenance procedures, and safety systems. White space documentation emphasises environmental conditions, configuration management, and change control procedures that support precise facility operations.
Future Evolution and Technology Integration
Emerging cooling technologies are blurring traditional boundaries between grey and white space areas as liquid cooling systems require infrastructure that spans both zones. The integration of advanced cooling technologies requires careful consideration of infrastructure zone design whilst maintaining operational efficiency and maintenance accessibility.
Energy storage technologies increasingly require installation within grey space areas whilst providing services that directly affect white space operations. The integration of battery storage systems requires coordination between infrastructure zones whilst maintaining safety, efficiency, and operational flexibility.
Automation technologies enable more sophisticated coordination between infrastructure zones, providing opportunities for optimised facility operations whilst reducing manual intervention requirements. The implementation of automation systems requires careful consideration of system interfaces, safety requirements, and operational procedures that span multiple infrastructure zones.
Sustainability technologies, including renewable energy systems and advanced monitoring capabilities, require coordination between infrastructure zones whilst supporting environmental objectives. The integration of sustainability technologies affects both system design and operational procedures, making comprehensive planning essential for successful implementation.
Edge computing requirements may influence traditional grey/white space boundaries as distributed computing infrastructure requires different design approaches. The evolution towards edge computing requires reconsideration of infrastructure zone design whilst maintaining the precision and reliability required for mission-critical operations.
The Integrated Approach: Optimising Infrastructure Zone Coordination
Our partnership with Qcloud enables AuditCo to deliver comprehensive grey/white space design and installation services that optimise coordination between infrastructure zones. This collaboration combines our expertise in quality assurance and system integration with Qcloud’s specialist knowledge of hyperscale infrastructure design, ensuring that grey/white space relationships support optimal facility performance.
The integrated approach begins with comprehensive analysis of operational requirements, maintenance procedures, and performance objectives that influence infrastructure zone design. This methodology ensures that grey/white space coordination supports both current operations and future expansion requirements whilst maintaining the efficiency and reliability required for hyperscale operations.
Design coordination services ensure that infrastructure zones are optimised for overall facility performance rather than individual system efficiency. This approach delivers facilities that demonstrate superior performance whilst maintaining the operational flexibility and maintenance accessibility required for long-term success.
Installation coordination ensures that grey and white space systems are commissioned and tested as integrated infrastructure rather than independent systems. This approach provides verification of system interactions, performance optimisation, and operational readiness that supports successful facility commissioning.
Quality assurance throughout the design and installation process ensures that infrastructure zone coordination meets design specifications whilst providing the documentation required for ongoing facility management. Our systematic approach to quality verification provides confidence in system performance whilst establishing the foundation for efficient operational procedures.
Conclusion: Infrastructure Zone Excellence for Operational Success
Understanding and optimising the relationship between grey and white space represents a fundamental requirement for successful hyperscale facility development. The coordination between infrastructure zones influences everything from system efficiency and operational costs to maintenance procedures and future expansion capabilities.
Our partnership with Qcloud enables AuditCo to deliver the comprehensive grey/white space design and installation services that hyperscale operators require for optimal facility performance. By combining deep technical expertise with systematic quality assurance, we help clients achieve infrastructure zone coordination that supports both current operations and future requirements.
The investment in professional grey/white space design and installation services represents essential preparation for decades of efficient facility operations. For hyperscale operators seeking to establish facilities that demonstrate superior performance whilst maintaining operational flexibility, comprehensive infrastructure zone planning provides the technical foundation for achieving these objectives.
AuditCo provides comprehensive audit, inspection, and compliance services for digital infrastructure projects worldwide. Our partnership with Qcloud enables integrated design-build-comply solutions that optimise grey/white space coordination for superior hyperscale facility performance. For more information about our infrastructure zone services, please contact our team at info@auditco.co.uk